In research, software tests are the area that is closest to IT development. The area of software development is also increasingly defined by the Scrum principle, which of course has an impact on testing as a management discipline. In this article I would like to describe in detail what these effects look like and go into this in more depth in my research.
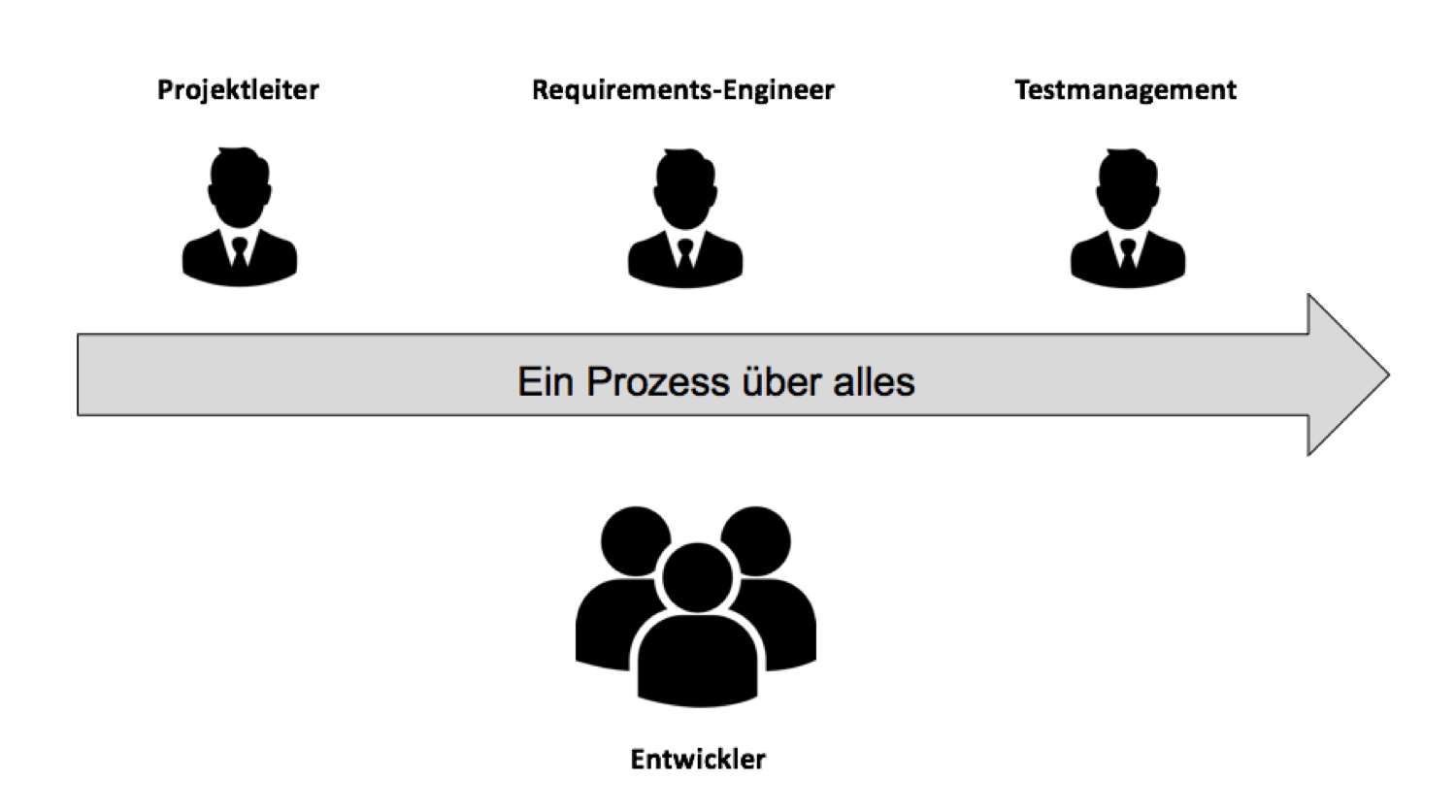
Baumgartner et al. (2013, p. 3) show in the figure above that Scrum one process for all roles Are defined. In the picture you can see how this one process combines the roles of the project manager, requirements engineer and tester. “Test” as a discipline no longer exists in isolation from Scrum. Rather, like the other roles, the tester becomes part of the overall agile process.
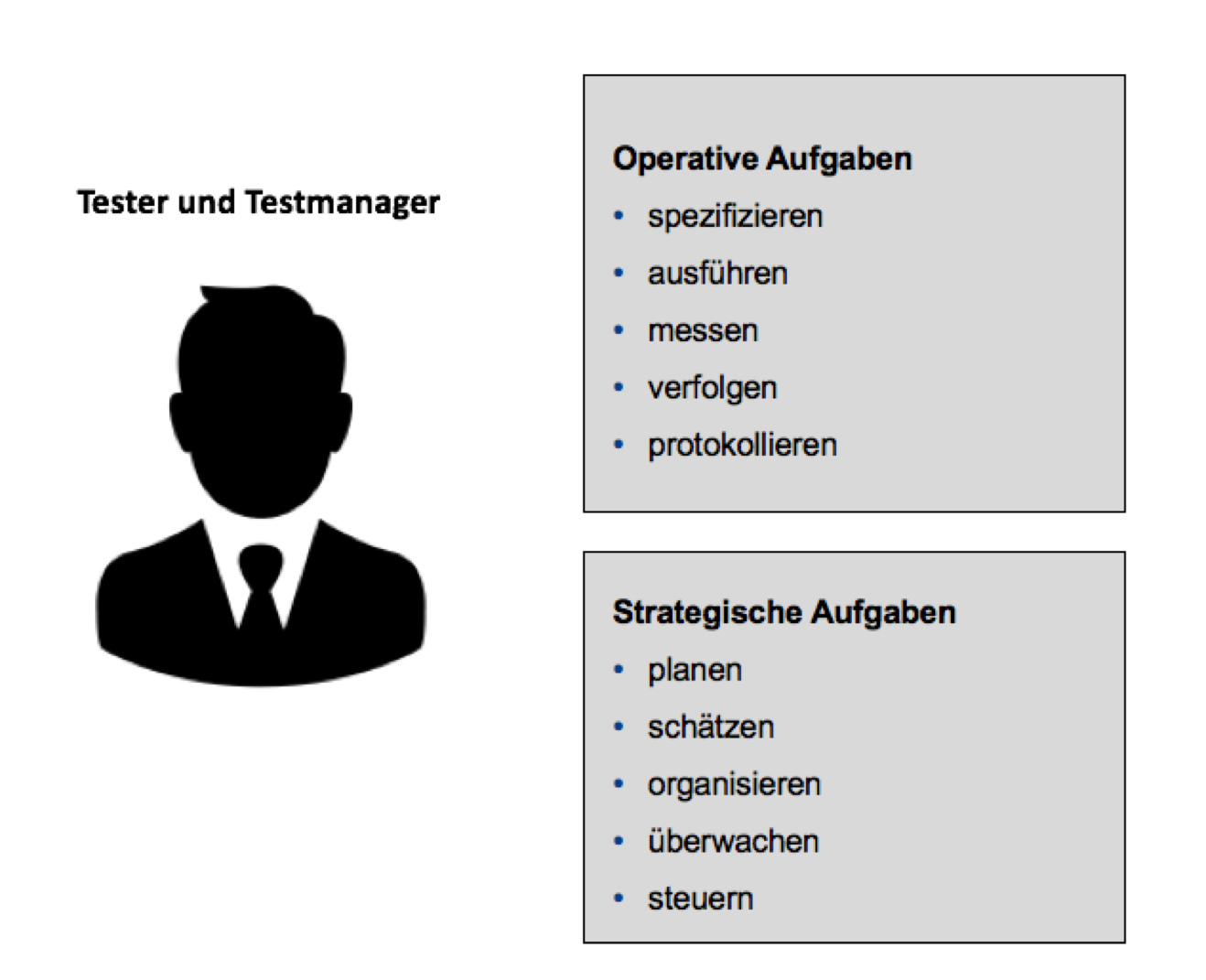
In the representation of Baumgartner et al. (2013, p. 101) we see how the role of the new, agile tester is split equally into the tasks of test manager and tester. Thus, one person or the agile department takes on operational tasks on the one hand – these tasks include the tests themselves, measurements, as well as logging and tracking – and, on the other hand, strategic tasks such as planning, estimating and organizing the tests .
Agile Test – The role of the tester in the team
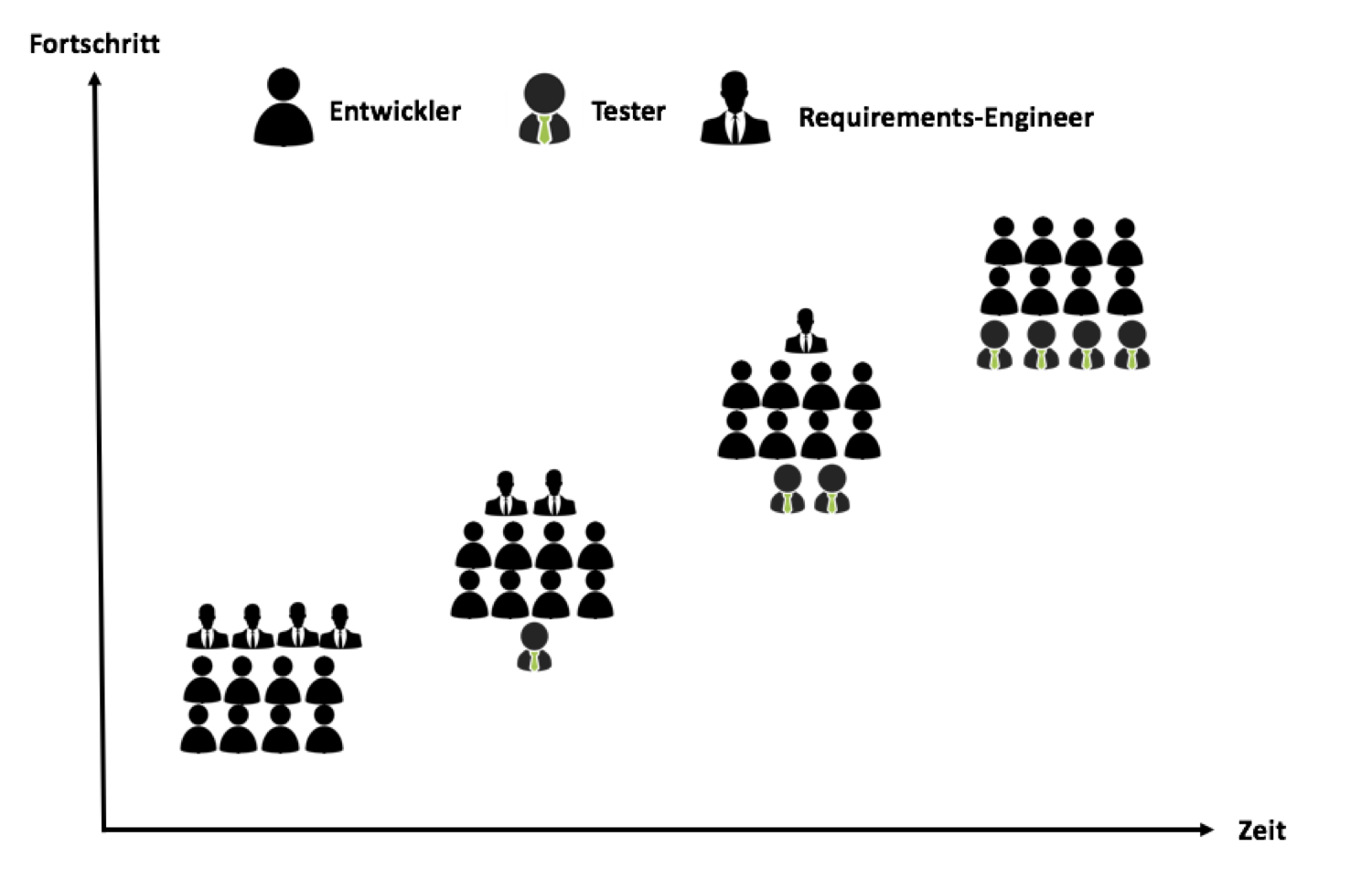
But where do we currently have to classify the tester in the entire team? Baumgartner et al. 2013, p.112 provide an answer in the diagram below: The tester is in close contact with the development team, which feeds him with information or which the tester gets by monitoring the process. He is also in direct contact with the PO (Product Owner) in order to be able to correctly evaluate the development based on the requirements set by the Product Owner, which in turn are specified by the stakeholders. Testers appreciate the Sprint planning now also reduce the testing effort and thus make an essential contribution to the product. As part of my research, I am reviewing these approaches. In his book, Baumgartner clarifies the relationships between the individual roles within Scrum: The tester checks the development based on the requirements of the PO.
In practice, there is a growing test effort in the course of the respective product development. However, according to Scrum, this growth is actually not beneficial, as the test effort should be constant throughout the process and should not increase towards the end, as can be seen in the figure below. In the first interviews we learn that testers work in advance and prepare the tests, so to speak, and estimate the effort. So the testing effort in the observing teams was still the same over the entire duration of the process. The quality was also very high at the beginning.
Basic principles of Agile Test
For this paragraph I am listing some tips for the agile test which I am going to use Wikipedia have found and summarize here.
- Quick feedback: 2 weeks or less
- High level of automation of the test
- Low overhead in the form of test management
- Dissolution of test roles (test manager, analyst, etc.)
- Dissolution of the test levels from the V-model (unit, integration, system …)
- Close cooperation in the team (feature teams, tester also writes code from time to time)
Baumgartner, M., Klonk, M., Pichler, H., Seidl, R., & Tanczos, S. (2013). Agile testing . Munich: Hanser Verlag.



