The Lean Startup method is on everyone’s lips and is described as best practice. The inventor Eric Ries describes how a product with few chapters can be tried out on the market. The author gives practical examples such as from Dropbox:
Dropbox had a landing page online. The founders bought several clicks via Google Adwords. Interested parties could enter their e-mail address in a mailing list in order to receive the beta version of the product when it was ready. The two founders collected 75,000 emails within a few hours. Only then was the Dropbox product built. Thus the idea was evaluated and implemented very favorably.
In my opinion, Lean Startup has three phases. While the first phase deals with testing assumptions and building a prototype, phase 2 looks for scaling and phase 3 for growth. In the following I would like to explain the three phases in more detail and make an excursus about landing pages.
Phase 1: testing the idea
Eric Ries recommends test cycles in an MVP (Minimal Product). This means that you should think about it: what do I at least have to do to evaluate the idea. He speaks of a problem-solution-fit (does the problem really exist and is our solution the right one?).
One example is a button in the online shop with a dummy function. As soon as the user clicks, a system measures the number of clicks and the user receives a message: We are currently in the process of building the function. In this way the question can be answered: “Will the function also be used?”
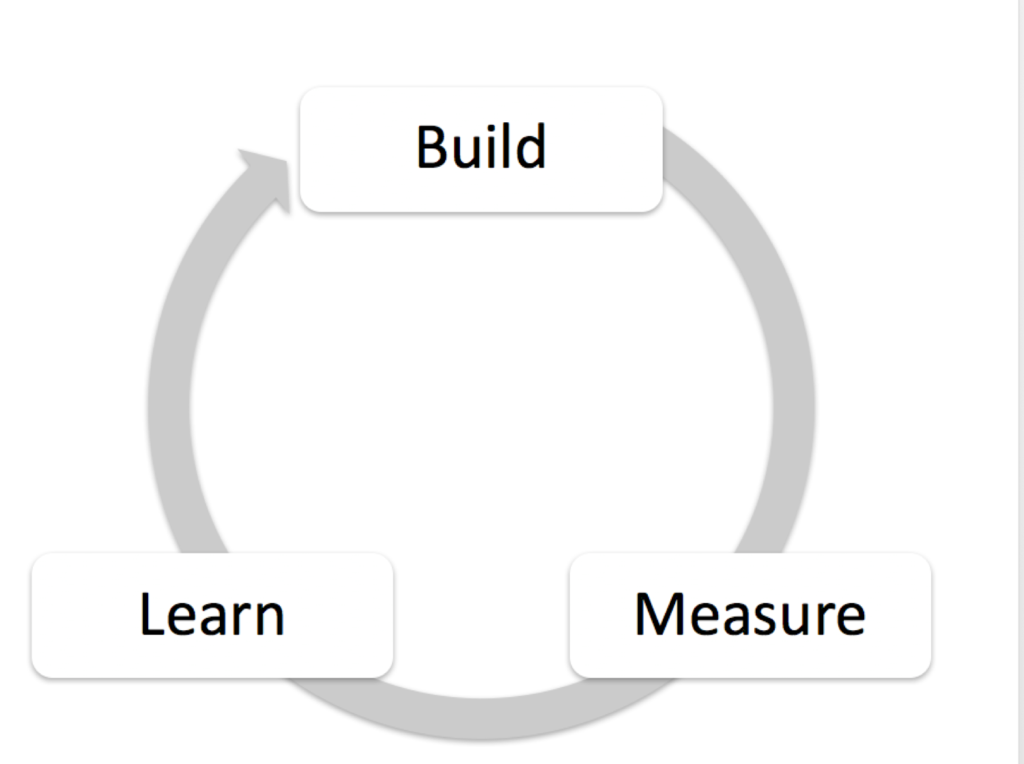
Lean Startup has the following steps:
- Build: A first product version or dummy function, e.g. prototype, landing page
- Measure: How can I measure success?
- Learn: What can I conclude from the data for the next prototype?
It is therefore important to start numerous experiments and learning processes in this step. Alternatives are also surveys and interviews in this step.
Excursus: testing the idea with a landing page
It is a very good way to evaluate ideas Landing page put on. Landing pages are compact websites that illuminate a topic or idea and contain a clear call to action such as registration for a newsletter. In order for an idea to be evaluated with such a website, it must be advertised using ad words, flyers, mailings, information material, QR codes or advertisements in magazines. Special advantages of landing pages are:
- Compact focus on the idea
- Can be used flexibly, e.g. different versions for different target groups and A / B tests
- often really very good conversion rates
- very flexible adaptable and changeable
- the success can be clearly measured by the conversions
Phase 2: scaling
In this step, confirmed assumptions / functions or parts of the product are to be built. The author recommends drawing up an innovation balance sheet in order to fine-tune the functions in the field test. The aim of this step is therefore to further develop each function and refine it in small steps using measurable numbers.
Important: Do not use numbers like growth or conversion. The author recommends a cohort analysis and A / B tests. The aim is that the influence of direct changes can be checked precisely. Think of it as if you were walking on an ice sheet (frozen lake) and after every step you think about: Should I go further or rather slightly to the right / left because I break in.
A / B tests are to be understood as follows: “A / B testing is a method used to compare two versions of a website or app to determine which is performing better. The two variants are called A and B and are shown to users at random. So some of the users get to the first version, others to the second. (Source Scanning sy ). A cohort analysis means dividing customers into segments and looking at the behavior of each customer group differently, e.g. according to age (teenagers, adults, retirees) or according to entry (Adwords, organic, Facebook).
Phase 3: growth
Phase 3 deals with the growth of the product. The author differentiates between three growth engines. The “sticky engine” means to keep customers who regularly generate sales. The viral engine increases the awareness of the product from person to person through word of mouth, which can save some marketing costs and the paid engine generates profits from existing customers, which in turn are used to acquire new customers (e.g. affiliate marketing).
According to the author, these three numbers are to be measured and increased through marketing. The focus of this phase is therefore on growing the product and increasing sales in three categories.
Conclusion
I find this method very useful and even quite academic. Science has long worked with hypotheses and variables. We have our marketplace Projektify.de also built with this method and have achieved success! We also use this method in innovation projects with customers in my professional life. Take a look at that Book by Eric Ries . Also read my article on agile product development.
Image source. Fotolia.de – purchased license
[werbung] [fotolia]


